題組內容
7. (15%) Enzymes serve as catalysts in many chemical reactions in living systems. The simplest such reactions transform a single substrate into a product with the help of an enzyme, which may be represented schematically as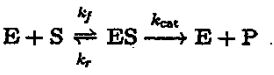
In this mechanism, the enzyme E is a catalyst, which only facilitates the reaction, so that its total concentration, free plus combined, [E] + [ES] = [E]o is a constant.
(b) (4%) Applying the steady-state approximation to ES, show that the initial rate V0 at which P is formed can be described by the Michaelis-Menten equation Vo=(Vmax*[S]0)/ ([S]0 +Km), where [S]0 is the concentration of the substrate and Vmax=kcat [E]0 is the maximum rate at which the product may be formed and Km = (kf+kcat)/kf is the MichaelisMenten constant.