題組內容
3.(Total=15%) Consider a communication system in which the received signal y(t)
is given by
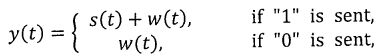
where w(t) is white Gaussian noise with (zero mean) power spectral density
N0/2 and s(t) is shown below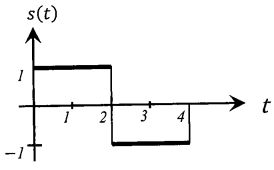
At the receiver, the received signal y(t) is passed through a filter with impulse
response h(t) = s(T-t). The output of the filter is sampled at time to that
- provides a decision statistic Y with
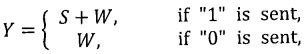
where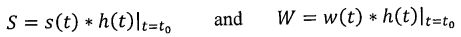 are the
filtered/sampled outputs of s(t) and w(t), respectively. The maximum
likelihood (ML) decision rule is then used based on Y to decide whether "I" or
"0" is sent. Assume the noise process is independent of which signal is sent.
are the
filtered/sampled outputs of s(t) and w(t), respectively. The maximum
likelihood (ML) decision rule is then used based on Y to decide whether "I" or
"0" is sent. Assume the noise process is independent of which signal is sent.