題組內容
(4, 10pts) Chemists are capable of modifying different structural moieties on substrates in order to optimize binding to the drug target. For example, a series of substrates were designed to bind to protease to function as protease inhibitors, and their binding thermodynamic properties were determined and summarized here. Three bars under each substrate refer to their values of AG°, AH°, and (-TAS°) of binding (adapted from J. Mol. Bio. 405, 11070 (2011)).
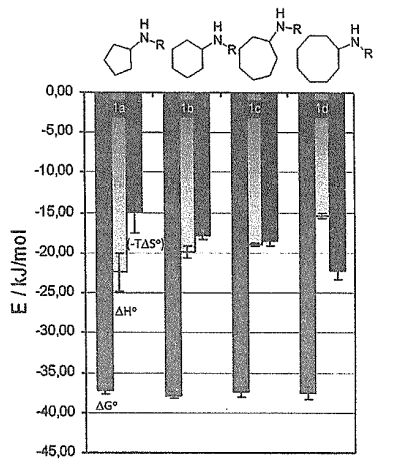
(4C, 4pts). As seen in the figure, surprisingly, there are no apparent change in Gibbs free energies of binding on all these modified substrates. Please propose a molecular model to explain this set of data.