題組內容
(6) (25%) Consider a discrete memoryless source (DMS) with the associated source alphabet X := {a, b, c, d, e,f, g}. Each source output is independenty selocted from C with the probability distribution Px given in Table 1. The goal of source coding for the DMS is to construct a code C that assigns cach symbol 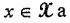 bit string
bit string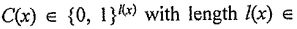 N. Its average length is defined as
N. Its average length is defined as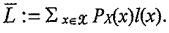 Moreover, the code is usually required to be uniquely decodable.
Moreover, the code is usually required to be uniquely decodable. 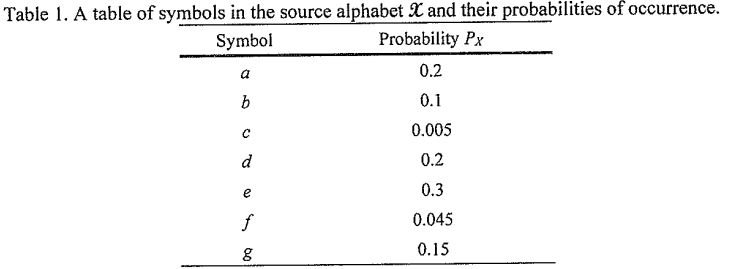 Please answer the following questions.
Please answer the following questions.
(b) (5%) A class of codes called the prefix-free codes can be decoded with no delay (hence sometimes also called instantareous codes). What is the definition for the prefix-free codes?
Every prefix-free code for the alphabet 9X with its codeword lengths  must satisfy the Kraftinequality. What is the Kraft inequality?
must satisfy the Kraftinequality. What is the Kraft inequality?
Assume that a code with its codeword lengths satisfies the Kraft inequality. Is it uniquely decodable? Does a uniquely decodable code have to satisfy the Kraft inequality?