題組內容
4. Heterogeneity (25 points)
Consider a one-period economy with competitive markets. There are mass one households and mass
one firins. The firms use labor in units of working hours, n, to produce consumption goods, and the
production function is: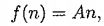
where A > 0 captures the productivity of firms. The housebold's utility is 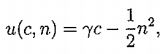
where the c is the consumption, n is the working hour, and the parameter,γ > O, captures the
importance of consumption to households. A household's income comes from working, and the wage
per hour is denoted by w. Thus, the household's budget constraint is
c = wn.
(b) (5 points) Now we extend the benchmark model to assume that housebolds are heterogeneous. Consider that half of the bouseholds are type 1, and half of the households are type 2, Type 1 and type 2 value consumptions differently, and this is captured by their difference in the parameter 7. Type I households' utility is
and type 2 households' utility is