題組內容
4. Heterogeneity (25 points)
Consider a one-period economy with competitive markets. There are mass one households and mass
one firins. The firms use labor in units of working hours, n, to produce consumption goods, and the
production function is: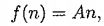
where A > 0 captures the productivity of firms. The housebold's utility is 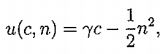
where the c is the consumption, n is the working hour, and the parameter,γ > O, captures the
importance of consumption to households. A household's income comes from working, and the wage
per hour is denoted by w. Thus, the household's budget constraint is
c = wn.
(c) (10 points) We further extend the model by introducing a government into the economy. The government charges a proportional tax on wage income. That is, suppose that a household's wage income is wn, then the government takes away tun from the household. The government transfers the tax revenue to all houscholds equally in a lump sum manner. How does the proportional tax on wage infuence the consumption equality ? Explain your answer.
? Explain your answer.