題組內容
2. The impurity level in a chemical used in laboratory experiments must not exceed
50 parts per million (ppm) in each batch. Each batch of the purchased chemical will
be tested to see if the requirement is met using the hypothesis H0:μ ≥50 vs.
H1:μ < 50, where 4 is the mean impurity level, Suppose that 100 samples are tested
from each batch, and the impurity measurements are normally distributed with mean
u = 50 and standard deviation σ = 2 ppm. (Hint: Use -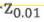 = -2.326 and the
standard normal c.d.f.Φ(-2)= 0.0228)
= -2.326 and the
standard normal c.d.f.Φ(-2)= 0.0228)
(B) If the chance of accepting a batch of chemical that does not meet the
standard is to be limited to no more than 1%, determine the critical value c so
that H0 can be rejected if  < c, where & is the mean impurity level of 100
samples. (6 marks)
< c, where & is the mean impurity level of 100
samples. (6 marks)